Starlink sent and received texts over a 4G/LTE connection between mobile phones via its latest generation of satellites, called v2mini, for the first time this month, following similar projects from Amazon, Apple, AST SpaceMobile, Huawei, and Lynk Global. Starlink—the satellite constellation operated by SpaceX—will offer text messaging to subscribers of at least eight different mobile-network operators around the world and may offer voice and data coverage without the need for the ground terminals its customers now use in “coming years,” Starlink’s U.S. partner T-Mobile said in a statement.
Starlink 本月首次通过其最新一代卫星 v2mini 通过手机之间的 4G/LTE 连接发送和接收文本,亚马逊、苹果、AST SpaceMobile、华为和 Lynk Global 也推出了类似项目。 Starlink——由 SpaceX 运营的卫星星座——将向全球至少八个不同移动网络运营商的用户提供短信服务,并可能提供语音和数据覆盖,而无需客户现在使用的地面终端。 ”Starlink 的美国合作伙伴 T-Mobile 在一份声明中表示。
The Starlink achievement is the latest example of how satellites and cellular base stations are converging. A handful of companies are exploiting cheaper satellite fabrication and launch costs, as well as adapting existing technologies such as beamforming, to bridge the several hundred kilometers between mobile phones and orbiting satellites. Among the many new wrinkles those companies have to iron out is the fact that for the first time, the towers themselves are the mobile component of the network: Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites move at tens of thousands of kilometers an hour, so they have little time to communicate with any one mobile phone on the Earth’s surface.
星链成就是卫星和蜂窝基站融合的最新例子。少数公司正在利用更便宜的卫星制造和发射成本,并采用波束成形等现有技术,以架起手机和轨道卫星之间数百公里的桥梁。这些公司必须解决的许多新问题之一是,塔本身首次成为网络的移动组件:低地球轨道(LEO)卫星以每小时数万公里的速度移动,因此它们几乎没有时间与地球表面的任何一部手机进行通信。
The companies competing to solve these problems have so far sent and received text messages on conventional phones via a commercial satellite (Huawei/China Telecom; Lynk Global; Apple/Globalstar) and performed voice and data calls over 5G via an experimental satellite (AST SpaceMobile) as IEEE Spectrumhas reported. Investors have taken notice: Lynk Global is going public in a deal that values the company at up to US $800 million while AT&T, Google, and Vodafone recently invested in AST SpaceMobile, which has a market capitalization of $674.6 million.
迄今为止,竞相解决这些问题的公司已通过商业卫星(华为/中国电信;Lynk Global;苹果/Globalstar)在传统手机上发送和接收短信,并通过实验卫星(AST SpaceMobile)通过 5G 进行语音和数据通话)正如 IEEE Spectrum 报道的那样。投资者已经注意到:Lynk Global 即将上市,该公司估值高达 8 亿美元,而 AT&T、Google 和沃达丰最近投资了 AST SpaceMobile,后者的市值为 6.746 亿美元。
“I recall many discussions 10 years ago where the mobile operators told the satellite people, ‘Your price points are way too high.’ This has totally changed due to more availability of the technology, more agile development, and a different approach to failure.”—ANDREAS KNOPP, UNIVERSITY OF THE BUNDESWEHR
“我记得 10 年前的许多讨论,移动运营商告诉卫星人员,‘你们的价格点太高了。’由于技术的可用性更高、开发更敏捷以及失败的处理方法不同,这种情况已经完全改变。 ”——安德烈亚斯·克诺普,德国联邦国防军大学
Until very recently, satellites could not connect to mobile phones hundreds of kilometers below. The sort of satellite phones people took on expeditions to more remote places have chunky antennas, require clear lines of sight to multiple satellites, and take a while to acquire a signal. Integrating terrestrial and satellite cellular networks isn’t as easy as moving between cell towers and handing off the signal from one to the next.
直到最近,卫星还无法连接到数百公里以下的手机。人们去更偏远的地方探险时使用的卫星电话有粗大的天线,需要与多颗卫星保持清晰的视线,并且需要一段时间才能获取信号。集成地面和卫星蜂窝网络并不像在蜂窝塔之间移动并将信号从一个蜂窝塔传递到另一个蜂窝塔那么容易。
Indeed, the task is so difficult that one research group built an experimental application to help an Internet-connected livestock truck equipped with its own computer switch to an onboard Starlink ground station when the truck loses the cellular network signal. Achieving a seamless integration of terrestrial and nonterrestrial networks is the ultimate goal, says study coauthor Melisa López, a wireless communications researcher at the University of Aalborg in Denmark.
事实上,这项任务非常困难,以至于一个研究小组开发了一个实验应用程序,帮助一辆配备自己的计算机的联网牲畜卡车在失去蜂窝网络信号时切换到车载星链地面站。研究合著者、丹麦奥尔堡大学无线通信研究员 Melisa López 表示,最终目标是实现地面和非地面网络的无缝集成。
Starlink doesn’t explain many details of its 4G connection, but existing commercial constellations reveal several of the building blocks of seamless satellite cellular connections, and researchers have published at least one promising lead for future constellations.
Starlink 没有解释其 4G 连接的许多细节,但现有的商业星座揭示了无缝卫星蜂窝连接的几个构建模块,研究人员已经发布了至少一个未来星座的有希望的线索。
Three Keys to Connecting Phones to Satellites
Instead of redesigning mobile phones to be more like satellite phones, companies are redesigning the satellite network to meet mobile phones more than halfway. They are making the antennas on the satellites much bigger in their scramble to turn satellites into cellphone towers. For example, AST SpaceMobile’s first satellites had antennas with surface areas of 64 square meters, followed by second generation satellites with 128 m2 antennas, with plans for going up to 400 m2. Starlink’s new v2mini satellite antennas are 6.21 m2, but Starlink plans even larger cellular-compatible satellites that it will launch when its larger Starship rocket is available.
将手机连接到卫星的三个关键公司不再将手机重新设计得更像卫星电话,而是重新设计卫星网络,以适应手机的一半以上。他们正在将卫星上的天线做得更大,以期将卫星变成手机信号塔。例如,AST SpaceMobile 的第一颗卫星的天线表面积为 64 平方米,随后的第二代卫星天线面积为 128 平方米,计划扩大到 400 平方米。 Starlink 的新型 v2mini 卫星天线面积为 6.21 平方米,但 Starlink 计划推出更大的蜂窝兼容卫星,当其更大的 Starship 火箭可用时,将发射这些卫星。
Companies are also making their satellites more like cellphone towers by flying them lower than before. For the first few decades of the space age, communications satellites were inserted into geosynchronous orbits much higher above the Earth, where they could cover a large portion of the planet’s surface for a relatively long period of time. However, those satellites handled far fewer devices than exist today.
公司还通过将卫星飞行得比以前更低,使卫星变得更像手机发射塔。在太空时代的最初几十年里,通信卫星被插入比地球高得多的地球同步轨道,在那里它们可以在相对较长的时间内覆盖地球表面的大部分地区。然而,这些卫星处理的设备比现在少得多。
The advent of smaller and cheaper satellites and cheaper launch costs in the last decade or so have enabled business models that rely on many cheaper satellites flown in low Earth orbit. These new satellites won’t last as long but will be better able to detect the weak signals from mobile phones on the surface and handle their growing traffic.
过去十年左右,更小、更便宜的卫星的出现以及更便宜的发射成本使得依赖许多在近地轨道飞行的更便宜的卫星的商业模式成为可能。这些新卫星的使用寿命不会那么长,但能够更好地检测地面手机发出的微弱信号并处理日益增长的流量。
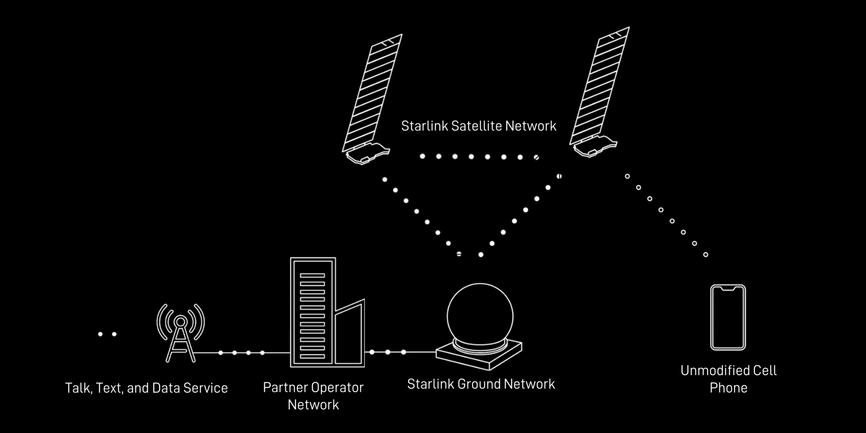
SpaceX’s Starlink network can connect directly to an off-the-shelf cellphone, potentially eliminating the need for bulky satellite phones.STARLINK
SpaceX 的 Starlink 网络可以直接连接到现成的手机,从而可能消除对笨重卫星电话的需求。STARLINK
“I recall many discussions 10 years ago where the mobile operators told the satellite people, ‘Your price points are way too high.’ This has totally changed due to more availability of the technology, more agile development, and a different approach to failure,” says Andreas Knopp, a signal processing engineer at the University of the Bundeswehr in Munich.
“我记得 10 年前的许多讨论,移动运营商告诉卫星人员,‘你们的价格太高了。’由于技术的可用性更高、开发更敏捷以及失败的处理方法不同,这种情况已经完全改变了, ”慕尼黑联邦国防军大学信号处理工程师 Andreas Knopp 说道。
Another contributor is improved beamforming, which is how a transmitting device calculates the best way to direct its signal to reach a particular recipient, without interfering with other recipients. That may involve bouncing a signal off a building or mountainside, from terrestrial towers, or it may involve precise targeting of a narrow, fast-moving signal, from a satellite moving tens of thousands of kilometers per hour.
另一个贡献者是改进的波束成形,这是发射设备如何计算将其信号引导至特定接收者而不干扰其他接收者的最佳方式的方式。这可能涉及从建筑物或山坡、地面塔反射信号,或者可能涉及从每小时数万公里移动的卫星精确瞄准狭窄、快速移动的信号。
More sophisticated beamforming can involve sending the same signals from multiple antennas so that the signal’s reinforce each other, a bit like when sound waves harmonize. Anyone who has tuned a home speaker system to provide the best sound at the point of a particular couch has done beamforming, probably with the help of sophisticated software in the background.
更复杂的波束成形可能涉及从多个天线发送相同的信号,以便信号相互增强,有点像声波协调一样。任何将家庭扬声器系统调整为在特定沙发上提供最佳声音的人都已经完成了波束成形,可能是在后台复杂软件的帮助下进行的。
In the future, it may be worth spreading the task of beamforming across even more satellites than now, write the authors of a pair of recent papers. A scenario floated in one of the studies is the use of more than two dozen tiny satellites flying in close formation to replicate the work done today by one cellular-compatible satellite. “Each of these satellites is now independent, with its own components. The main aspect is this synchronization algorithm, which has to align frequency, phase, and the time for the signals to arrive coherently,” says Diego Tuzi, a graduate student studying signal processing at the University of the Bundeswehr who, together with Knopp, is a coauthor on one of those recent papers.
最近两篇论文的作者写道,未来,可能值得将波束成形任务分散到比现在更多的卫星上。其中一项研究中提出的一个场景是,使用两打以上紧密编队飞行的微型卫星来复制目前由一颗蜂窝兼容卫星所做的工作。 “这些卫星现在都是独立的,有自己的组件。主要方面是这种同步算法,它必须调整频率、相位和信号一致到达的时间,”德国联邦国防军大学研究信号处理的研究生迭戈·图齐 (Diego Tuzi) 说道,他与克诺普 (Knopp) 一起,最近发表的其中一篇论文的合著者。
For now, what Starlink and its competitors are offering is very little, though it is a necessary step. “It’s better than nothing,” says Thomas Delamotte, another coauthor on the recent paper and a signal processing engineer at the University of the Bundeswehr, “but if you want to have a long-term perspective we will need new approaches to make 6G ubiquitous.”
目前,星链及其竞争对手提供的服务非常少,尽管这是必要的一步。 “这总比没有好,”最近论文的另一位合著者、德国联邦国防军大学的信号处理工程师托马斯·德拉莫特 (Thomas Delamotte) 说道,“但如果你想拥有长远的眼光,我们将需要新的方法来让 6G 无处不在。 ”。


 Optimisus
Optimisus Optimisus
Optimisus Optimisus
Optimisus Thecryptoupdates
Thecryptoupdates DogeHome
DogeHome The Crypto Times
The Crypto Times Coincu
Coincu Optimisus
Optimisus Coin_Gabbar
Coin_Gabbar






















