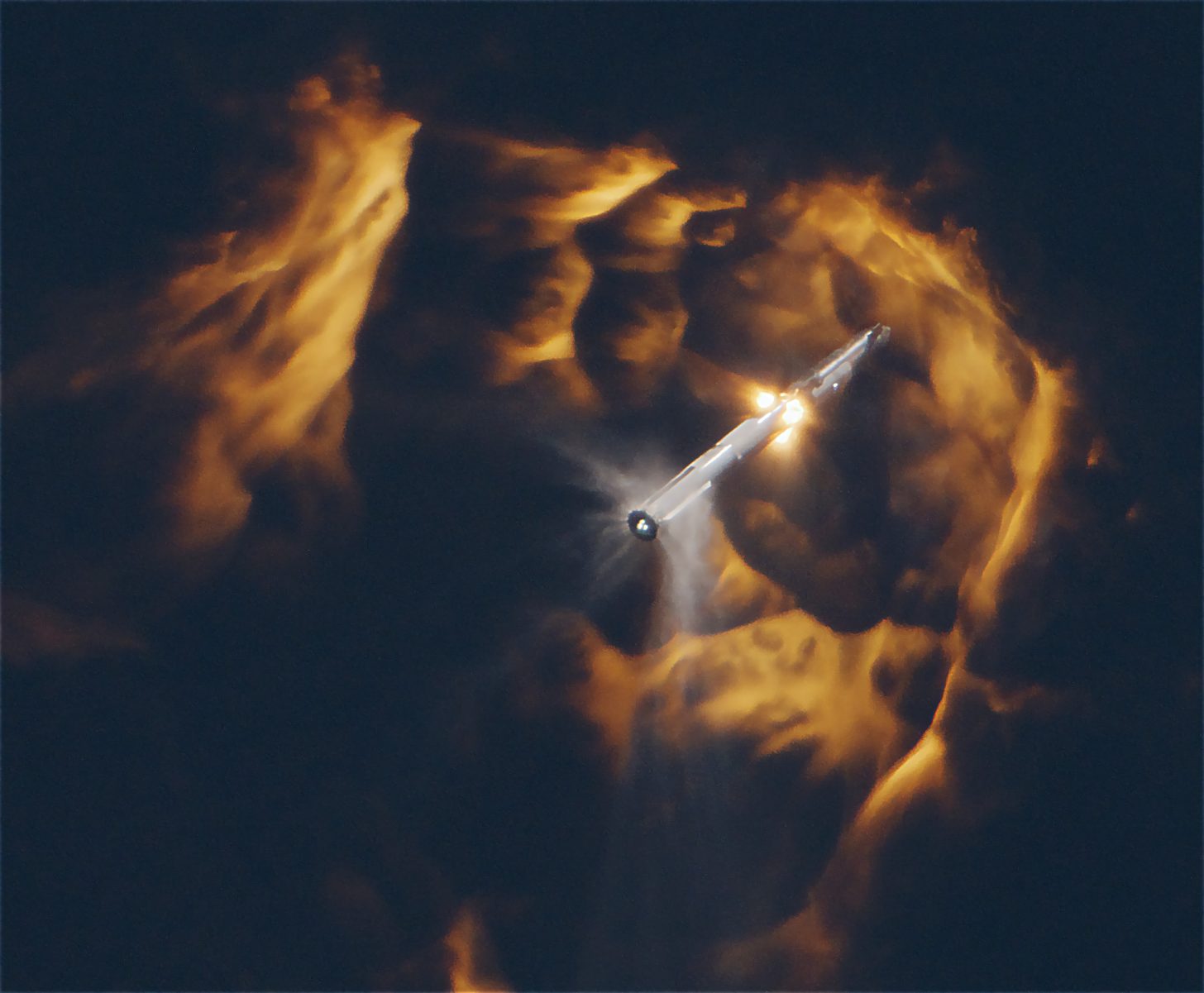

SpaceX's first Starship test flight in April carries the risk of significantly delaying the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Artemis program to develop a sustainable human presence on the Moon, according to a report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO). NASA's Artemis III flight is currently planned to take off in 2025, and the GAO's report shares that several portions of SpaceX's Human Landing System (HLS) development are taking longer than NASA programs typically do based on average historical data. Other key constraints identified for a 2025 launch include delays with the new spacesuits that Axiom Space is designing for lunar use.
会計検査院(GAO)の報告書によると、4月に行われたスペースX社の初のスターシップ試験飛行は、月面での人類の持続可能な存在を開発するためのアメリカ航空宇宙局(NASA)のアルテミス計画を大幅に遅らせるリスクを伴うという。 NASAのアルテミスIII飛行は現在2025年に離陸する予定であり、GAOの報告書は、SpaceXの有人着陸システム(HLS)開発のいくつかの部分が、平均的な過去のデータに基づいてNASAプログラムが通常行うよりも長い時間がかかっていることを共有している。 2025年の打ち上げに向けて特定されたその他の重要な制約には、アクシオム・スペースが月面での使用のために設計している新しい宇宙服の遅れが含まれる。
In-Space Propellant Transfer Remains Key Hurdle To Successful Starship Demonstration Says GAO Report
SpaceX's mission architecture for its Starship HLS lunar lander involves launching a fuel depot to space and then filling it up. Once the depot is full, the HLS lander will dock with it to fill up and then start its journey to the Moon. According to the GAO, demonstrating in-space propellant transfer requires successfully launching Starship into orbit. SpaceX's April Starship test flight ended up delaying key demonstrations. to make them uncomfortably close to a 2025 Artemis III launch.
宇宙での推進剤輸送は依然として宇宙船実証成功への主要なハードルであるとGAOレポートSpaceXの月着陸船Starship HLSのミッションアーキテクチャには、燃料貯蔵庫を宇宙に打ち上げてから燃料を充填することが含まれる。デポが満杯になると、HLS 着陸船がドッキングして満杯になり、月への旅を開始します。 GAO によると、宇宙での推進剤輸送を実証するには、スターシップを軌道に打ち上げることが必要です。スペースXの4月のスターシップ試験飛行は結局、主要なデモンストレーションを遅らせる結果となった。 2025年のアルテミスIII打ち上げに不快なほど近づくことになる。
The report outlines that for its April Starship test, SpaceX had planned to successfully demonstrate Starship ascent, flight of the second stage stacked on the first stage and stage separation. However, company officials informed the agency that a fire inside the rocket caused its autonomous flight termination system to destroy the rocket and prematurely end the test.
報告書は、4月のスターシップテストで、スペースXがスターシップの上昇、第1ステージに積み重ねられた第2ステージの飛行、およびステージの分離を成功裏に実証する計画を立てていたことを概説している。しかし、同社関係者らはロケット内部の火災により自律飛行停止システムがロケットを破壊し、試験が途中で終了したと当局に伝えた。
SpaceX and NASA have delayed multiple "key events" for the HLS program to 2024, says the GAO, with eight out of 13 key events delayed by six to 13 months. SpaceX has to complete eight key events between November 2023 and the Artemis III flight, and this assessment was made before this month's orbital test flight that demonstrated stage separation and second-stage Starship engine ignition.
GAOによると、SpaceXとNASAはHLS計画の複数の「重要イベント」を2024年まで延期し、13の重要イベントのうち8件が6~13か月延期されたという。 SpaceXは、2023年11月からアルテミスIII飛行までの間に8つの主要イベントを完了する必要があり、この評価は、段分離と第2段スターシップエンジン点火を実証した今月の軌道試験飛行の前に行われた。
The delays might also have safety implications for the HLS program as they will squeeze the timeline that NASA has to work with to ensure that Starship meets human spaceflight requirements, states the GAO. According to NASA and HLS officials, SpaceX has to demonstrate that Starship can make it to orbit before it can progress to other milestones, such as a pre-Artemis III uncrewed test and in-space propellant transfer.
スターシップが有人宇宙飛行の要件を満たしていることを確認するためにNASAが協力しなければならないスケジュールが圧迫されるため、遅延はHLSプログラムの安全性にも影響を与える可能性があるとGAOは述べている。 NASAとHLS関係者によると、スペースX社は、アルテミスIII以前の無人試験や宇宙での推進剤移送など、他のマイルストーンに進む前に、スターシップが軌道に乗れることを証明する必要があるという。
However, HLS officials were confident that a successful test flight would accelerate SpaceX's design process, enabling the firm to lock in Starship's design. After the April test flight, NASA officials were uncertain whether Starship could meet the Artemis III December 2025 deadline, with the HLS program schedule requiring adjustments post-April.
しかし、HLS関係者は、試験飛行が成功すればSpaceXの設計プロセスが加速され、同社がStarshipの設計を定着させることが可能になると確信していた。 4月の試験飛行後、HLSプログラムのスケジュールは4月以降の調整が必要となるため、NASA関係者はスターシップがアルテミスIIIの2025年12月の期限に間に合うかどうか不透明だった。
The primary technical work areas that might cause a delay include the Raptor engine and the fuel depot. Operating the Raptor at certain performance levels is key for the engine's certification, and should it remain uncertified, then an alternative engine system cannot be developed in time. Talking to the GAO, SpaceX's representatives shared that they were able to collect valuable data for tanking and other operations after the April test. They added that SpaceX has assembled and tested hundreds of engines as part of an iterative design approach.
遅延の原因となる可能性のある主な技術作業領域には、ラプター エンジンと燃料貯蔵所が含まれます。ラプターを特定の性能レベルで動作させることがエンジンの認証の鍵であり、認証されないままだと、代替エンジン システムの開発が間に合わなくなります。スペースXの代表者らはGAOとのインタビューで、4月の実験後にタンキングやその他の作戦のための貴重なデータを収集できたと語った。彼らは、SpaceXが反復設計アプローチの一環として何百ものエンジンを組み立て、テストしたと付け加えた。
For the on-orbit fuel storage system, the report outlines that program documentation shares that SpaceX has made little progress in maturing these technologies. Key systems that SpaceX has to develop include
軌道上燃料貯蔵システムについては、SpaceX がこれらの技術の成熟においてほとんど進歩していないことがプログラム文書で共有されていると報告書は概説している。 SpaceX が開発しなければならない主要なシステムには次のものがあります。
According to the GAO, some of the systems that SpaceX has to develop are:
GAO によると、SpaceX が開発しなければならないシステムには次のようなものがあります。
Those systems include docking sensors and mechanisms (to identify, locate, and then physically align the HLS Starship and the tanker Starship for fluid transfer); propellant measurement (to gauge the amount of propellant in the tanks and how much was transferred); and storage capability to mitigate fuel loss in space.
これらのシステムには、ドッキング センサーとメカニズム (流体移送のために HLS Starship とタンカー Starship を識別、位置特定し、物理的に位置合わせするため) が含まれています。推進剤の測定(タンク内の推進剤の量と移送された量を測定するため)。宇宙での燃料損失を軽減する貯蔵能力。
The report was written before SpaceX's November Starship test, which saw successful stage separation and engine ignition. Since then, footage from the facilities in Texas shows significant activity as SpaceX prepares Starship for its next test flight.
この報告書は、ステージ分離とエンジン点火に成功したスペースX社の11月のスターシップ試験前に書かれた。それ以来、テキサス州の施設からの映像には、スペースXがスターシップを次の試験飛行に向けて準備する際の重要な活動が示されている。


 Crypto Daily™
Crypto Daily™ crypto.news
crypto.news Crypto Daily™
Crypto Daily™ DogeHome
DogeHome Optimisus
Optimisus Crypto Intelligence
Crypto Intelligence BlockchainReporter
BlockchainReporter Cryptopolitan_News
Cryptopolitan_News DogeHome
DogeHome






















