How is Bitcoin priced?
Market forces called supply and demand influence Bitcoin’s price. The price typically decreases when there are more sellers or vice versa.
Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency that is not issued by any government or legal body, in contrast to fiat currencies, such as the United States dollar, the British pound, the euro and the Japanese yen. To create, store and move BTC, a dispersed network of users and cryptographic protocols are required.
Investors carry out their commercial transactions directly instead of using an intermediary. The peer-to-peer Bitcoin network removes trade restrictions and streamlines commerce. Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the world’s first cryptocurrency in 2008, which was launched in January 2009.
The number of businesses accepting Bitcoin contributes to its usability and perceived value. However, its price has been subject to significant volatility and is influenced by factors such as media coverage, investor sentiment and regulatory news, which have led to rapid price fluctuations. Even at the height of its popularity, finding precise answers to common questions is challenging, such as, what determines Bitcoin’s price? Who sets Bitcoin’s price? And does Bitcoin have intrinsic value?
The same supply and demand market dynamics that affect the price of other goods and services also determine the price of Bitcoin. Prices will probably rise if there are more buyers than sellers or vice-versa. Furthermore, it is important to note that the price of Bitcoin is not determined by a single entity, nor is it traded in a single location, such as on a stock exchange.
Instead, each market or exchange determines its price based on supply, demand and other factors, such as technological advancements, security measures and regulatory developments.
What factors could impact Bitcoin’s price?
Various factors impacting Bitcoin’s price include the supply and demand of BTC, competition from other cryptocurrencies, news, cost of production and regulation.
Supply and demand
Those with a background in economics know the law of supply and demand, which states that supply and demand market forces work together to determine the market price and the quantity of a specific commodity. For instance, the demand for an economic good declines as the price increases and sellers produce more or vice versa.
The fundamental economic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role in Bitcoin’s valuation. Bitcoin has a 21 million coin hard cap on its supply, introducing scarcity to the digital currency. Miners will no longer receive new Bitcoin for verifying transactions once that cap is reached.
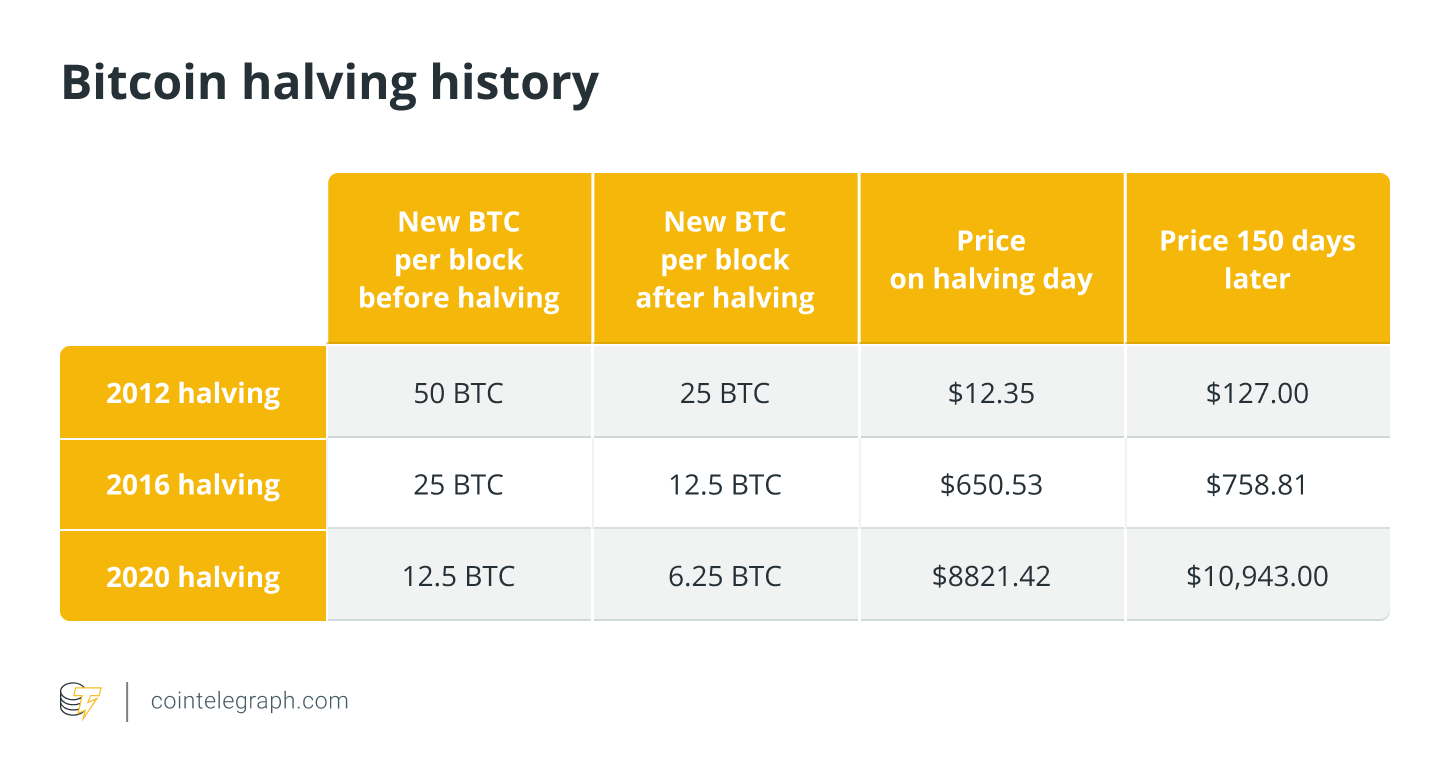
Similarly, an event called the Bitcoin halving halves the reward for mining new blocks every four years (approximately), reducing the rate at which new BTC enters the market supply. As supply growth slows, if demand remains steady or increases, it can lead to higher Bitcoin prices.
Competition and news
Bitcoin competes with numerous alternative cryptocurrencies, such as Ether (ETH) and Dogecoin (DOGE), each with unique features that attract investor interest. Additionally, news and media coverage can significantly impact investor sentiment, driving price fluctuations based on perceptions of Bitcoin’s future prospects.
Cost of production
The cost of producing Bitcoin encompasses not only direct expenses like infrastructure and electricity for miners but also indirect costs related to the complexity of the cryptographic challenges they must solve. These costs contribute to establishing a baseline or “break-even” point for miners, affecting the lowest price at which they might consider it economically viable to mine Bitcoin.
This break-even point is often referred to as the “floor price” in the context of Bitcoin mining, representing the minimum price at which mining Bitcoin can be profitable when considering operational costs.
Moreover, the Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of its cryptographic puzzles in response to the overall mining power, influencing how quickly new Bitcoin are produced. These adjustments can either decelerate or accelerate the rate of Bitcoin creation, affecting the overall supply and, subsequently, its market price.
Regulation
Cryptocurrency regulations are constantly changing, with some countries taking a friendly approach to crypto, such as El Salvador, which made Bitcoin legal tender in 2021, and others taking a less friendly approach to crypto, such as China, which formally banned crypto transactions outright in 2019. Regulatory developments can significantly impact Bitcoin’s market dynamics, creating uncertainty that may affect its price.
When authorities introduce restrictive measures, it can exert downward pressure on Bitcoin’s price. Conversely, regulatory actions that enhance market accessibility, like approving spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in the United States and improving security measures, can foster greater market participation and potentially lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price.
Why is the Bitcoin price so volatile?
Uncertainty regarding the intrinsic value of Bitcoin and BTC’s future price makes it a highly volatile asset.
The amount of new Bitcoin entering the supply decreases steadily every four years in the halving, decreasing the asset’s inflation rate over time. According to CompaniesMarketcap, Bitcoin is the 10th-largest asset by market cap at the time of writing and is no longer a niche asset but a significant player in the broader financial landscape. Moreover, media coverage can disproportionately affect asset prices, and this phenomenon is not exclusive to Bitcoin.
However, the immediacy and ubiquity of information today, facilitated by digital media and social media platforms, means that news (positive or negative) can rapidly influence investor sentiment and, consequently, asset prices across the board. This effect is amplified in highly speculative markets where investor sentiment plays a crucial role, as is often the case with cryptocurrencies.
The approval of U.S.-based spot Bitcoin ETFs on Jan. 11 significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price, attracting institutional capital and increasing demand. As a result, at the time of writing, the price of Bitcoin has surged by 33% since Jan. 11 as traditional finance investors and institutions rallied to invest.
Considering this high volatility, can the Bitcoin price go to zero? Such a scenario is highly unlikely but technically possible under extreme conditions, such as a catastrophic technological failure undermining the blockchain’s security or a complete loss of confidence by all users and investors. However, these scenarios are highly improbable due to Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, widespread adoption, and the robustness of its underlying technology.
Moreover, layer-2 innovations like the Lightning Network aim to solve usability and scalability problems, which could improve the value proposition of Bitcoin. Unlike Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard, which facilitates the creation of tokens and smart contracts on its network, Bitcoin, by design, does not natively support complex smart contracts or token standards.
Nonetheless, innovative solutions are being developed to extend Bitcoin’s capabilities in this area. For instance, developments like the RSK (Rootstock) platform are bridging this gap by introducing smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Additionally, the BRC-20 token standard represents an innovative approach to introducing tokenization capabilities directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. As an experimental standard, BRC-20 aims to enable the creation, minting and transfer of fungible tokens, akin to how the ERC-20 standard functions on Ethereum and other Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible networks.
What will happen if Bitcoin's price crashes to zero?
If BTC's price drops to zero, it will impact the traders, institutional investors, price of other digital currencies, cryptocurrency enterprises and the whole financial system.
Now, assuming that BTC's price declines to zero, it will impact the price of other cryptocurrencies. As a result, many investors could just withdraw (completely or substantially) to reduce losses, depending on their type of investment.
Large institutional investors may be particularly at risk because more and more have made larger investments to diversify their portfolios. The most exposed would be those who invested more recently at high prices or in crypto derivatives, and they would need to liquidate other assets to fulfill margin calls.
Customers may lose faith in a system that appears to be crumbling, affecting cryptocurrency enterprises like Coinbase, Binance, etc., that depend on customers for transaction flow to generate revenue and funding/investments to grow. Investments in these companies may also stop altogether or significantly decline. Additionally, such enterprises may no longer be able to hire, pay or attract the personnel necessary to run and expand them.
Furthermore, the contagion may, at least temporarily, have an impact on the rest of the financial system due to:
- Downward pressure on other assets such as those sold in a fire sale to raise money to meet obligations, such as paying remuneration, margin calls, maintaining premises, etc., and
- The accumulation of bad debt or non-performing loans due to payment defaults amid the loss of revenue and capital.


 DogeHome
DogeHome Optimisus
Optimisus Crypto News Land
Crypto News Land Optimisus
Optimisus Cryptopolitan_News
Cryptopolitan_News Cryptopolitan
Cryptopolitan






















