How is Bitcoin priced?
ビットコインの価格はどのように決まるのでしょうか?
Market forces called supply and demand influence Bitcoin’s price. The price typically decreases when there are more sellers or vice versa.
需要と供給と呼ばれる市場の力がビットコインの価格に影響を与えます。通常、売り手が多い場合、またはその逆の場合、価格は下がります。
Bitcoin (BTC) is a cryptocurrency that is not issued by any government or legal body, in contrast to fiat currencies, such as the United States dollar, the British pound, the euro and the Japanese yen. To create, store and move BTC, a dispersed network of users and cryptographic protocols are required.
ビットコイン (BTC) は、米ドル、英国ポンド、ユーロ、日本円などの法定通貨とは対照的に、政府や法人によって発行されていない暗号通貨です。 BTC を作成、保存、移動するには、ユーザーの分散ネットワークと暗号化プロトコルが必要です。
Investors carry out their commercial transactions directly instead of using an intermediary. The peer-to-peer Bitcoin network removes trade restrictions and streamlines commerce. Satoshi Nakamoto proposed the world’s first cryptocurrency in 2008, which was launched in January 2009.
投資家は仲介業者を介さずに直接商取引を実行します。ピアツーピアのビットコイン ネットワークは取引制限を取り除き、商取引を合理化します。サトシ・ナカモトは2008年に世界初の仮想通貨を提案し、2009年1月に発売されました。
The number of businesses accepting Bitcoin contributes to its usability and perceived value. However, its price has been subject to significant volatility and is influenced by factors such as media coverage, investor sentiment and regulatory news, which have led to rapid price fluctuations. Even at the height of its popularity, finding precise answers to common questions is challenging, such as, what determines Bitcoin’s price? Who sets Bitcoin’s price? And does Bitcoin have intrinsic value?
ビットコインを受け入れる企業の数は、ビットコインの使いやすさと認識される価値に貢献します。しかし、その価格は大幅な変動にさらされており、メディア報道、投資家心理、規制ニュースなどの要因の影響を受け、急速な価格変動を引き起こしています。ビットコインの人気が最高潮に達しているときでも、ビットコインの価格は何によって決まるのかなど、よくある質問に対する正確な答えを見つけるのは困難です。ビットコインの価格は誰が設定するのでしょうか?そして、ビットコインには本質的な価値があるのでしょうか?
The same supply and demand market dynamics that affect the price of other goods and services also determine the price of Bitcoin. Prices will probably rise if there are more buyers than sellers or vice-versa. Furthermore, it is important to note that the price of Bitcoin is not determined by a single entity, nor is it traded in a single location, such as on a stock exchange.
他の商品やサービスの価格に影響を与えるのと同じ需要と供給の市場力学が、ビットコインの価格も決定します。売り手より買い手が多い場合、またはその逆の場合、価格はおそらく上昇します。さらに、ビットコインの価格は単一の主体によって決定されるわけではなく、証券取引所などの単一の場所で取引されるわけでもないことに注意することが重要です。
Instead, each market or exchange determines its price based on supply, demand and other factors, such as technological advancements, security measures and regulatory developments.
代わりに、各市場または取引所は、需要、供給、および技術の進歩、セキュリティ対策、規制の発展などのその他の要因に基づいて価格を決定します。
What factors could impact Bitcoin’s price?
どのような要因がビットコインの価格に影響を与える可能性がありますか?
Various factors impacting Bitcoin’s price include the supply and demand of BTC, competition from other cryptocurrencies, news, cost of production and regulation.
ビットコインの価格に影響を与えるさまざまな要因には、BTCの需要と供給、他の仮想通貨との競争、ニュース、生産コスト、規制などが含まれます。
Supply and demand
需要と供給
Those with a background in economics know the law of supply and demand, which states that supply and demand market forces work together to determine the market price and the quantity of a specific commodity. For instance, the demand for an economic good declines as the price increases and sellers produce more or vice versa.
経済学の知識がある人は、市場の需要と供給が連携して特定の商品の市場価格と数量を決定するという需要と供給の法則を知っています。たとえば、価格が上昇して売り手がより多く生産するか、その逆になると、経済財の需要は減少します。
The fundamental economic principle of supply and demand plays a crucial role in Bitcoin’s valuation. Bitcoin has a 21 million coin hard cap on its supply, introducing scarcity to the digital currency. Miners will no longer receive new Bitcoin for verifying transactions once that cap is reached.
需要と供給という基本的な経済原理は、ビットコインの評価において重要な役割を果たします。ビットコインには供給量に2,100万コインのハードキャップがあり、デジタル通貨に希少性をもたらしています。この上限に達すると、マイナーはトランザクションを検証するために新しいビットコインを受け取ることができなくなります。
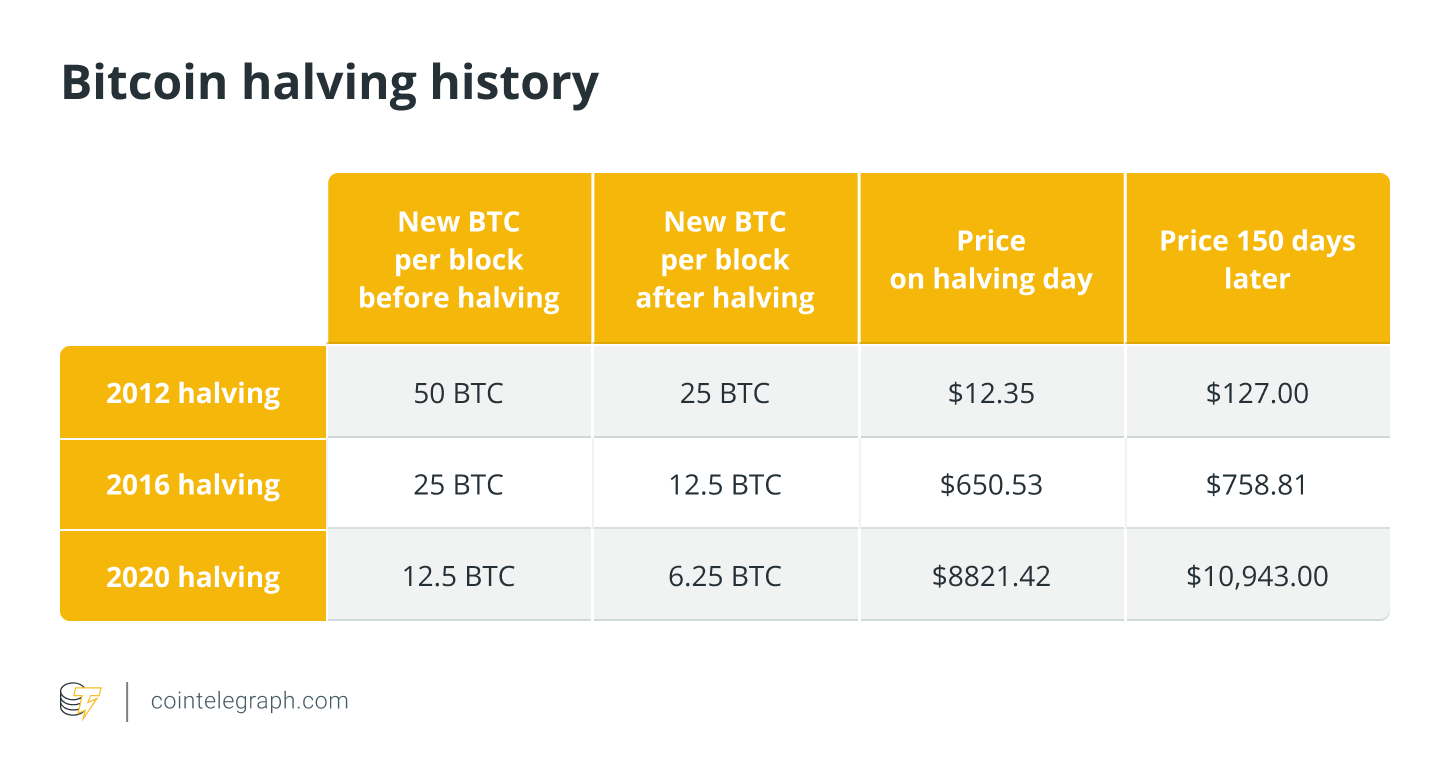
Similarly, an event called the Bitcoin halving halves the reward for mining new blocks every four years (approximately), reducing the rate at which new BTC enters the market supply. As supply growth slows, if demand remains steady or increases, it can lead to higher Bitcoin prices.
同様に、ビットコインの半減期と呼ばれるイベントでは、新しいブロックのマイニングに対する報酬が (およそ) 4 年ごとに半減し、新しい BTC が市場に供給される速度が低下します。供給の伸びが鈍化しても、需要が安定するか増加すると、ビットコイン価格の上昇につながる可能性があります。
Competition and news
競争とニュース
Bitcoin competes with numerous alternative cryptocurrencies, such as Ether (ETH) and Dogecoin (DOGE), each with unique features that attract investor interest. Additionally, news and media coverage can significantly impact investor sentiment, driving price fluctuations based on perceptions of Bitcoin’s future prospects.
ビットコインは、イーサ (ETH) やドージコイン (DOGE) など、投資家の興味を引く独自の機能を備えた多数の代替暗号通貨と競合します。さらに、ニュースやメディアの報道は投資家心理に大きな影響を与え、ビットコインの将来見通しの認識に基づいて価格変動を引き起こす可能性があります。
Cost of production
生産コスト
The cost of producing Bitcoin encompasses not only direct expenses like infrastructure and electricity for miners but also indirect costs related to the complexity of the cryptographic challenges they must solve. These costs contribute to establishing a baseline or “break-even” point for miners, affecting the lowest price at which they might consider it economically viable to mine Bitcoin.
ビットコインの生産コストには、マイナー向けのインフラストラクチャや電力などの直接的な費用だけでなく、解決しなければならない暗号化の課題の複雑さに関連する間接的な費用も含まれます。これらのコストは、マイナーにとってのベースラインまたは「損益分岐点」の確立に貢献し、ビットコインのマイニングが経済的に実行可能であると彼らが考える最低価格に影響を与えます。
This break-even point is often referred to as the “floor price” in the context of Bitcoin mining, representing the minimum price at which mining Bitcoin can be profitable when considering operational costs.
この損益分岐点は、ビットコイン マイニングの文脈では「下限価格」と呼ばれることが多く、運用コストを考慮した場合にビットコインのマイニングが利益を得ることができる最低価格を表します。
Moreover, the Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of its cryptographic puzzles in response to the overall mining power, influencing how quickly new Bitcoin are produced. These adjustments can either decelerate or accelerate the rate of Bitcoin creation, affecting the overall supply and, subsequently, its market price.
さらに、ビットコイン ネットワークは、全体的なマイニング能力に応じて暗号パズルの難易度を調整し、新しいビットコインが生成される速度に影響を与えます。これらの調整により、ビットコインの生成速度が減速または加速され、全体的な供給と、その後の市場価格に影響を与える可能性があります。
Regulation
規制
Cryptocurrency regulations are constantly changing, with some countries taking a friendly approach to crypto, such as El Salvador, which made Bitcoin legal tender in 2021, and others taking a less friendly approach to crypto, such as China, which formally banned crypto transactions outright in 2019. Regulatory developments can significantly impact Bitcoin’s market dynamics, creating uncertainty that may affect its price.
仮想通貨の規制は常に変化しており、2021年にビットコインを法定通貨としたエルサルバドルのように、仮想通貨に対して友好的なアプローチをとる国もあれば、2021年に仮想通貨取引を正式に全面禁止した中国のように、仮想通貨に対してあまり友好的ではないアプローチを取る国もある。 2019. 規制の動向はビットコインの市場動向に大きな影響を与え、価格に影響を与える可能性のある不確実性を生み出す可能性があります。
When authorities introduce restrictive measures, it can exert downward pressure on Bitcoin’s price. Conversely, regulatory actions that enhance market accessibility, like approving spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in the United States and improving security measures, can foster greater market participation and potentially lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price.
当局が制限措置を導入すると、ビットコインの価格に下落圧力がかかる可能性があります。逆に、米国における現物ビットコイン上場投資信託(ETF)の承認やセキュリティ対策の改善など、市場へのアクセスを強化する規制措置は、市場への参加を促進し、ビットコイン価格の上昇につながる可能性があります。
Why is the Bitcoin price so volatile?
なぜビットコインの価格はこれほど不安定なのでしょうか?
Uncertainty regarding the intrinsic value of Bitcoin and BTC’s future price makes it a highly volatile asset.
ビットコインの本質的価値とBTCの将来価格に関する不確実性により、ビットコインは非常に不安定な資産となっています。
The amount of new Bitcoin entering the supply decreases steadily every four years in the halving, decreasing the asset’s inflation rate over time. According to CompaniesMarketcap, Bitcoin is the 10th-largest asset by market cap at the time of writing and is no longer a niche asset but a significant player in the broader financial landscape. Moreover, media coverage can disproportionately affect asset prices, and this phenomenon is not exclusive to Bitcoin.
新たに供給されるビットコインの量は、半減期の4年ごとに着実に減少し、時間の経過とともに資産のインフレ率が低下します。 CompaniesMarketcap によると、本稿執筆時点でビットコインは時価総額で 10 番目に大きい資産であり、もはやニッチな資産ではなく、より広範な金融環境において重要な役割を果たしています。さらに、メディアの報道は資産価格に不釣り合いな影響を与える可能性があり、この現象はビットコインに限ったものではありません。
However, the immediacy and ubiquity of information today, facilitated by digital media and social media platforms, means that news (positive or negative) can rapidly influence investor sentiment and, consequently, asset prices across the board. This effect is amplified in highly speculative markets where investor sentiment plays a crucial role, as is often the case with cryptocurrencies.
しかし、デジタルメディアやソーシャルメディアプラットフォームによって促進された今日の情報の即時性と遍在性は、ニュース(肯定的または否定的)が投資家心理に急速に影響を与え、その結果として全体の資産価格に影響を与える可能性があることを意味します。この影響は、仮想通貨の場合と同様に、投資家の心理が重要な役割を果たす投機性の高い市場で増幅されます。
The approval of U.S.-based spot Bitcoin ETFs on Jan. 11 significantly impacted Bitcoin’s price, attracting institutional capital and increasing demand. As a result, at the time of writing, the price of Bitcoin has surged by 33% since Jan. 11 as traditional finance investors and institutions rallied to invest.
1月11日に米国を拠点とするスポットビットコインETFが承認されたことはビットコインの価格に大きな影響を与え、機関投資家を惹きつけ需要を増加させた。その結果、本稿執筆時点で、伝統的な金融投資家や機関が投資に結集するなか、ビットコインの価格は1月11日以来33%上昇した。
Considering this high volatility, can the Bitcoin price go to zero? Such a scenario is highly unlikely but technically possible under extreme conditions, such as a catastrophic technological failure undermining the blockchain’s security or a complete loss of confidence by all users and investors. However, these scenarios are highly improbable due to Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, widespread adoption, and the robustness of its underlying technology.
このボラティリティの高さを考慮すると、ビットコインの価格はゼロになる可能性があるでしょうか?このようなシナリオは可能性は非常に低いですが、ブロックチェーンのセキュリティを損なう壊滅的な技術的障害や、すべてのユーザーや投資家の信頼を完全に失うような極端な状況下では技術的に可能です。ただし、ビットコインの分散型の性質、広範な普及、およびその基盤となるテクノロジーの堅牢性を考慮すると、これらのシナリオは非常にありそうもないことです。
Moreover, layer-2 innovations like the Lightning Network aim to solve usability and scalability problems, which could improve the value proposition of Bitcoin. Unlike Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard, which facilitates the creation of tokens and smart contracts on its network, Bitcoin, by design, does not natively support complex smart contracts or token standards.
さらに、ライトニング ネットワークのようなレイヤー 2 イノベーションは、ユーザビリティとスケーラビリティの問題を解決することを目的としており、これによりビットコインの価値提案が向上する可能性があります。ネットワーク上でトークンやスマート コントラクトの作成を容易にするイーサリアムの ERC-20 トークン標準とは異なり、ビットコインは設計上、複雑なスマート コントラクトやトークン標準をネイティブにサポートしていません。
Nonetheless, innovative solutions are being developed to extend Bitcoin’s capabilities in this area. For instance, developments like the RSK (Rootstock) platform are bridging this gap by introducing smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
それにもかかわらず、この分野でビットコインの機能を拡張する革新的なソリューションが開発されています。たとえば、RSK (Rootstock) プラットフォームのような開発は、ビットコイン エコシステムにスマート コントラクト機能を導入することで、このギャップを埋めています。
Additionally, the BRC-20 token standard represents an innovative approach to introducing tokenization capabilities directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. As an experimental standard, BRC-20 aims to enable the creation, minting and transfer of fungible tokens, akin to how the ERC-20 standard functions on Ethereum and other Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible networks.
さらに、BRC-20 トークン標準は、ビットコイン ブロックチェーンに直接トークン化機能を導入する革新的なアプローチを表しています。実験的な標準として、BRC-20 は、ERC-20 標準がイーサリアムやその他のイーサリアム仮想マシンと互換性のあるネットワーク上でどのように機能するかに似た、代替トークンの作成、鋳造、転送を可能にすることを目的としています。
What will happen if Bitcoin's price crashes to zero?
ビットコインの価格がゼロに暴落したらどうなるでしょうか?
If BTC's price drops to zero, it will impact the traders, institutional investors, price of other digital currencies, cryptocurrency enterprises and the whole financial system.
BTCの価格がゼロに下落すると、トレーダー、機関投資家、他のデジタル通貨の価格、仮想通貨企業、そして金融システム全体に影響が及びます。
Now, assuming that BTC's price declines to zero, it will impact the price of other cryptocurrencies. As a result, many investors could just withdraw (completely or substantially) to reduce losses, depending on their type of investment.
さて、BTCの価格がゼロまで下落すると仮定すると、他の仮想通貨の価格に影響を与えることになります。その結果、多くの投資家は、投資の種類に応じて、損失を減らすために(完全にまたは大幅に)撤退することができます。
Large institutional investors may be particularly at risk because more and more have made larger investments to diversify their portfolios. The most exposed would be those who invested more recently at high prices or in crypto derivatives, and they would need to liquidate other assets to fulfill margin calls.
ポートフォリオを多様化するために大規模な投資を行う投資家が増えているため、大規模な機関投資家は特にリスクにさらされる可能性があります。最も危険にさらされているのは、最近高価格や仮想通貨デリバティブに投資した人たちで、マージンコールを満たすために他の資産を清算する必要があるだろう。
Customers may lose faith in a system that appears to be crumbling, affecting cryptocurrency enterprises like Coinbase, Binance, etc., that depend on customers for transaction flow to generate revenue and funding/investments to grow. Investments in these companies may also stop altogether or significantly decline. Additionally, such enterprises may no longer be able to hire, pay or attract the personnel necessary to run and expand them.
顧客は崩壊しつつあるように見えるシステムに対する信頼を失い、収益を生み出すためのトランザクションフローや成長のための資金/投資を顧客に依存しているCoinbaseやBinanceなどの仮想通貨企業に影響を与える可能性があります。これらの企業への投資が完全に停止されるか、大幅に減少する可能性もあります。さらに、そのような企業は、経営や拡大に必要な人材を雇用したり、給与を支払ったり、引きつけたりすることができなくなる可能性があります。
Furthermore, the contagion may, at least temporarily, have an impact on the rest of the financial system due to:
さらに、感染は少なくとも一時的に、以下の理由により金融システムの他の部分に影響を与える可能性があります。
- Downward pressure on other assets such as those sold in a fire sale to raise money to meet obligations, such as paying remuneration, margin calls, maintaining premises, etc., and
- The accumulation of bad debt or non-performing loans due to payment defaults amid the loss of revenue and capital.
報酬の支払い、マージンコール、施設の維持などの義務を果たすための資金を調達するために投げ売りで売却された資産など、他の資産に対する下方圧力。
収益と資本の損失の中での支払い不履行による不良債権または不良債権の蓄積。


 DogeHome
DogeHome Coin_Gabbar
Coin_Gabbar Coincu
Coincu BlockchainReporter
BlockchainReporter CoinPedia News
CoinPedia News TheNewsCrypto
TheNewsCrypto CFN
CFN






















